The Different Types Of AI.
AI, short for Artificial Intelligence, has become an integral part of our lives, from our smartphones to our cars. But do you ever wonder about the different types of AI that exist? In this article, we will explore the various categories of AI, ranging from narrow AI that specializes in specific tasks to general AI that possesses human-like intelligence. So buckle up and get ready to dive into the fascinating world of AI!
The Different Types of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly evolving field that encompasses a wide range of technologies and capabilities. As AI continues to advance, different types of AI have emerged, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will explore the various types of AI and delve into their definitions, characteristics, examples, limitations, challenges, and ethical considerations.
This image is property of www.simplilearn.com.
1. Narrow AI
1.1 Definition
Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, refers to AI systems that are designed to perform specific tasks or solve particular problems within a predefined scope. Unlike general AI, narrow AI is focused on a specific domain and lacks the ability to generalize its knowledge and skills to different areas.
1.2 Characteristics
Narrow AI systems are designed to excel in a specific task or set of tasks. They operate within a limited context and are not capable of autonomously learning or adapting to new situations. These systems typically rely on predefined rules and algorithms to make decisions and perform their designated functions.
1.3 Examples
Examples of narrow AI include voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, recommendation algorithms used by online platforms like Netflix and Amazon, and autonomous vehicles equipped with computer vision systems.
1.4 Limitations
One of the main limitations of narrow AI is its lack of flexibility and adaptability. These systems can only operate within their defined scope and struggle when faced with tasks or problems outside their area of expertise. Additionally, narrow AI systems are highly dependent on the quality and quantity of data they receive, and their performance may suffer if the data is incomplete or biased.
2. General AI
2.1 Definition
General AI, also known as strong AI, refers to AI systems that possess human-level intelligence and are capable of understanding, learning, and reasoning across a wide range of domains and tasks. Unlike narrow AI, general AI aims to replicate human cognitive abilities and exhibit a high degree of autonomy and adaptability.
2.2 Characteristics
General AI systems have the capacity to understand complex concepts, learn from experience, and apply their knowledge to solve unfamiliar problems. These systems are capable of reasoning, logical thinking, and decision-making based on a comprehensive understanding of the world.
2.3 Examples
While true general AI does not yet exist, there are ongoing efforts to develop systems that exhibit human-level intelligence. Prominent examples include research projects such as OpenAI’s GPT-3, which has demonstrated impressive language generation capabilities, and DeepMind’s AlphaGo, the AI program that defeated world champion Go players.
2.4 Challenges
Developing general AI poses significant challenges, as it requires creating systems that can fully comprehend and reason about the world in a way that is comparable to human intelligence. Achieving human-level performance across a wide range of tasks remains a grand challenge in AI research.
This image is property of www.edureka.co.
3. Superintelligent AI
3.1 Definition
Superintelligent AI refers to AI systems that surpass human intelligence across all domains and tasks. These systems possess cognitive capabilities that far exceed those of any human and have the potential to outperform humans in virtually every intellectual endeavor.
3.2 Characteristics
Superintelligent AI systems would possess an extraordinary degree of cognitive abilities, such as enhanced problem-solving skills, vast knowledge acquisition, and rapid learning capabilities. These systems would be able to surpass human creativity and innovation, leading to unprecedented advancements in various fields.
3.3 Benefits
The potential benefits of superintelligent AI are immense. Such systems could accelerate scientific discovery, revolutionize healthcare, solve complex global challenges, and greatly enhance the overall human experience. They could provide invaluable assistance in fields like climate modeling, drug design, and space exploration.
3.4 Concerns
However, the development of superintelligent AI also raises significant concerns. The potential risks associated with creating systems that surpass human intelligence need to be carefully addressed. The question of how to align the goals and values of superintelligent AI with human values and ensure its safe and ethical deployment is a critical area of research and debate.
4. Weak AI
4.1 Definition
Weak AI, also known as narrow AI, is a type of AI that is designed to perform specific tasks or solve particular problems within a limited domain. While weak AI systems can excel in their designated tasks, they lack the ability to exhibit true intelligence or understand the broader context beyond their specific programming.
4.2 Examples
Examples of weak AI systems are abundant in our daily lives. Voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, chatbots used for customer service, and recommendation systems used by online platforms are all examples of weak AI. These systems are designed to perform specific functions and are not capable of autonomous learning or reasoning beyond their predefined capabilities.
4.3 Applications
Weak AI finds applications in various domains, including healthcare, finance, marketing, and entertainment. In healthcare, AI diagnostic systems can analyze medical data to aid in disease diagnosis and treatment planning. In finance, algorithmic trading systems utilize AI to make data-driven investment decisions. In marketing, AI-powered recommendation systems personalize content and suggestions based on user preferences.
4.4 Limitations
Despite their utility, weak AI systems have several limitations. They lack comprehensive understanding, context awareness, and the ability to generalize knowledge. These systems heavily rely on data quality, and their performance may be affected by biased or incomplete datasets. Additionally, weak AI systems are typically domain-specific and cannot adapt to new tasks without extensive reprogramming or customization.
This image is property of imageio.forbes.com.
5. Strong AI
5.1 Definition
Strong AI, also known as general AI, represents AI systems that exhibit human-level intelligence across a wide range of domains and tasks. Unlike weak AI, which is designed for specific functions, strong AI possesses the ability to understand complex concepts, reason, learn, and apply knowledge across different domains.
5.2 Capabilities
Strong AI systems have the capability to learn, reason, and understand the world in a manner similar to human intelligence. These systems can analyze complex data, comprehend natural language, and adapt to new situations and tasks. They have the potential to exhibit creativity, problem-solving abilities, and consciousness.
5.3 Challenges
Developing strong AI systems presents significant challenges. Creating machines that possess human-level intelligence and cognitive capabilities is a complex task that requires advancements in fields such as machine learning, natural language processing, and cognitive science. Additionally, ensuring the ethical and responsible deployment of strong AI systems remains a critical concern.
5.4 Ethical Considerations
The development of strong AI raises important ethical considerations. Questions of autonomy, accountability, and responsibility arise when creating machines that possess advanced intelligence. Ensuring that strong AI systems align with human values, do not infringe upon individual rights, and operate ethically is of utmost importance in the development and deployment of such systems.
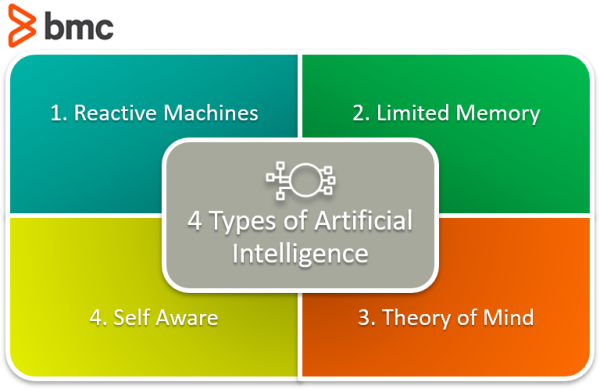
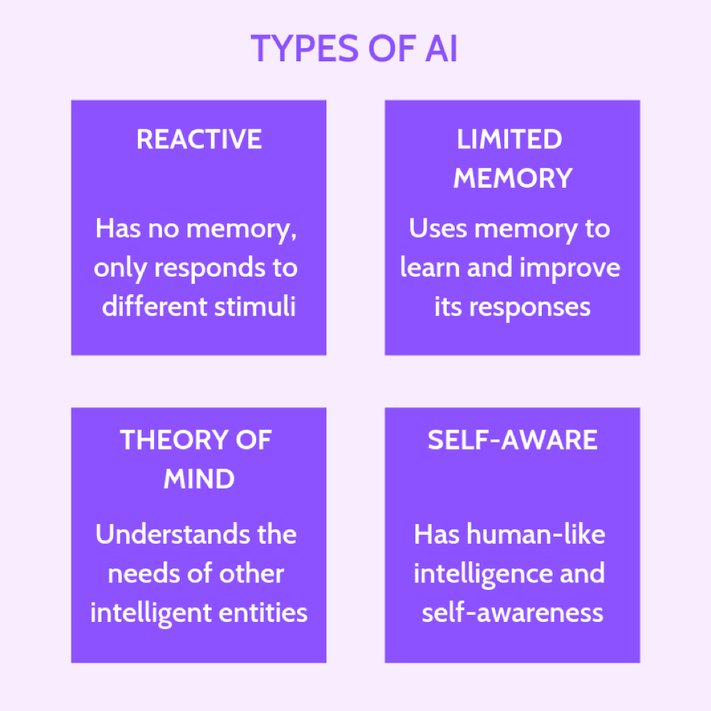
6. Reactive Machines
6.1 Definition
Reactive machines are a type of AI system that operates solely in the present moment, reacting to and executing specific tasks based on current input. These machines lack memory or the ability to store and recall past experiences, which limits their capabilities to the immediate task at hand.
6.2 Functionality
Reactive machines rely on predefined rules and algorithms to respond to specific stimuli. They do not have the capacity to learn from previous experiences or adapt to new situations. These systems are designed for highly focused and specific tasks, optimizing their efficiency and responsiveness to immediate inputs.
6.3 Advantages
Reactive machines offer certain advantages in terms of simplicity, speed, and resource efficiency. By focusing only on the immediate task, these systems can respond quickly without the need for extensive processing or memory allocation. They are particularly useful in applications that require real-time operations, such as robotics, automated control systems, and gaming AI.
6.4 Limitations
However, the limitations of reactive machines become apparent when faced with complex or dynamic situations. Their lack of memory prevents them from learning from past experiences, making them ill-equipped for tasks that require adaptation, reasoning, or long-term planning. Reactive machines are typically only proficient in the specific tasks they are programmed to execute and struggle when confronted with unfamiliar scenarios.

This image is property of s7280.pcdn.co.
7. Limited Memory AI
7.1 Definition
Limited Memory AI is a type of AI that combines the capabilities of reactive machines with the ability to store and recall past experiences to make improved decisions. These AI systems have a limited memory capacity that allows them to learn from previous encounters and adjust their behavior accordingly.
7.2 Features
Limited Memory AI systems can retain a subset of past experiences or data, enabling them to make informed decisions based on historical information. This memory capacity enhances their ability to adapt to changing circumstances and improve their performance over time. These systems can learn from mistakes and refine their responses based on past encounters.
7.3 Applications
Limited Memory AI finds applications in various domains where adaptive decision-making is crucial. For example, in self-driving cars, AI algorithms can store and learn from past traffic situations to improve their navigation and response to different driving conditions. In customer service chatbots, limited memory AI enables more personalized and context-aware interactions by learning from previous customer interactions.
7.4 Challenges
Despite their advantages, limited memory AI systems face challenges when dealing with large-scale or continuous learning tasks. The capacity of their memory may limit their ability to handle vast amounts of data or adapt to long-term trends effectively. Balancing memory capacity, computational requirements, and generalization capabilities remain ongoing challenges in the development of limited memory AI.
8. Theory of Mind AI
8.1 Definition
Theory of Mind AI refers to AI systems that possess the ability to understand not only their own mental state but also the mental states of others. These systems can infer beliefs, intentions, desires, and emotions, allowing them to perceive and interact with humans in a more socially intelligent manner.
8.2 Conceptual Understanding
Theory of Mind AI aims to replicate one of the fundamental aspects of human intelligence – the ability to attribute mental states to oneself and others. These systems can understand that others have different beliefs, thoughts, and emotions, enabling more nuanced and contextually appropriate interactions with humans.
8.3 Implications
Theory of Mind AI has significant implications for fields such as human-robot interaction, social robotics, and virtual assistants. Machines equipped with theory of mind capabilities can better understand and respond to human emotions, intentions, and social cues. This enhances the human-like interaction and makes these systems more adaptable and personalized.
8.4 Ethical Considerations
As theory of mind AI becomes more prominent, ethical considerations arise regarding privacy, consent, and the potential for manipulation. Machines that understand human mental states raise questions about the proper usage of this understanding and respecting individual boundaries. Ensuring transparent and ethical deployment of theory of mind AI systems is crucial to preserve trust and privacy.
This image is property of www.scnsoft.com.
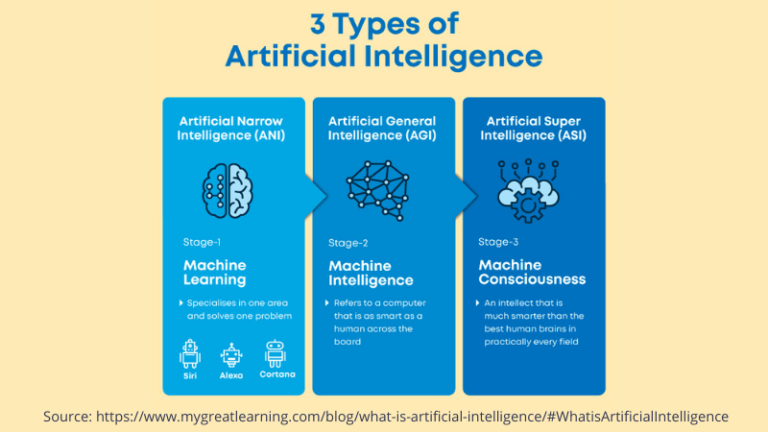
10. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
10.1 Definition
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) refers to AI systems that are designed for specialized tasks within a specific domain. These systems excel in a limited set of pre-defined tasks but lack the ability to exhibit general intelligence or understand beyond their designated area.
10.2 Applications
ANI systems find applications in various domains, such as healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and transportation. In healthcare, ANI is used for medical imaging analysis, diagnosis, and treatment planning. In finance, ANI powers algorithmic trading and fraud detection systems. In cybersecurity, ANI aids in detecting and mitigating threats through anomaly detection and pattern recognition.
10.3 Advantages
ANI systems offer several advantages, including high accuracy and efficiency in performing their designated tasks. By focusing on a specific domain, these systems can optimize their performance and provide valuable insights or solutions. ANI is widely implemented in industries where precise and specialized expertise is required.
10.4 Challenges
However, ANI has limitations in terms of adaptability and generalization. These systems cannot apply their knowledge or skills to unrelated domains or tasks beyond their specific programming. Moreover, ANI heavily relies on the quality and availability of data, and its performance may be affected by biased or incomplete datasets. Striking a balance between specialization and versatility remains a challenge in ANI development.
In conclusion, the field of AI encompasses various types with distinct characteristics and applications. Narrow AI, General AI, Superintelligent AI, Weak AI, Strong AI, Reactive Machines, Limited Memory AI, Theory of Mind AI, and Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) each have their unique attributes and implications. As AI continues to advance, understanding these different types is essential for navigating the possibilities and challenges presented by AI technologies.