The Challenges Of AI

Imagine living in a world where artificial intelligence is capable of solving complex problems, revolutionizing industries, and enhancing our everyday lives. While AI brings about incredible opportunities, it also presents us with a unique set of challenges. As we embark on this journey towards a more intelligent future, it is crucial to understand and address these hurdles. From ethical considerations to job displacement and the potential for biased decision-making, the challenges of AI demand our attention and careful navigation. In this article, we will explore these hurdles and delve into the complexities of AI, uncovering the obstacles that lie ahead on our path to harnessing its full potential.

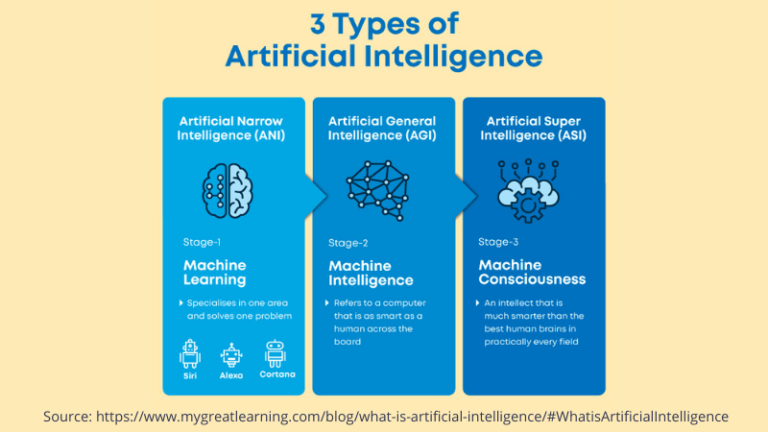
This image is property of cdn.elearningindustry.com.
Ethical Challenges
Bias in AI Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems rely on data to make decisions, but this data may not always be free from bias. If AI algorithms are trained on biased or incomplete datasets, they can perpetuate and even amplify existing inequalities and discrimination. For example, facial recognition technology has been found to have higher error rates for women and people with darker skin tones, leading to potential biases in areas such as criminal justice or hiring decisions. It is essential to address this bias in AI decision-making to ensure fairness and equal treatment for all individuals.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The widespread use of AI technologies raises concerns about the privacy and security of personal data. AI algorithms often require access to large amounts of data, including personal information, to function effectively. This poses a risk of unauthorized access, misuse, or exploitation of sensitive data. Additionally, AI systems that gather and analyze data in real-time, such as in smart cities or surveillance systems, raise concerns about constant surveillance and potential infringements on individuals’ privacy rights. It is crucial to establish robust data protection measures and develop AI systems that prioritize privacy to address these concerns.
Impact on Workforce and Employment
AI has the potential to automate a wide range of tasks and jobs, which can lead to significant changes in the workforce landscape. While AI can improve efficiency and productivity, it also raises concerns about job displacement and unemployment. Certain industries and occupations, such as manufacturing or customer service, may face significant disruptions as AI technologies replace human workers. Additionally, the adoption of AI may require workers to acquire new skills and adapt to changing job requirements. It is important to carefully manage these transitions, ensuring that the impact on the workforce is taken into account and adequate support and retraining opportunities are provided.
Accountability and Responsibility
As AI systems become more autonomous and make decisions that have a direct impact on individuals and society, the question of accountability and responsibility arises. Who is responsible if an AI system makes a mistake or causes harm? AI technologies can be complex, making it difficult to assign clear responsibility. In some cases, the responsibility may lie with the developers, while in others, it may be the users or even the AI system itself. Establishing clear accountability frameworks and defining the responsibilities of different stakeholders is crucial to ensure transparency, fairness, and trust in AI systems.
Technical Challenges
Data Quality and Availability
The performance of AI systems relies heavily on the quality and availability of data. Data used to train AI algorithms must be accurate, representative, and free from biases. However, obtaining high-quality data can be challenging, especially in cases where data is scarce or unavailable. Additionally, ensuring the ongoing availability of relevant and up-to-date data presents further technical challenges. Addressing data quality and availability issues is crucial to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of AI systems.
Interpretability and Explainability
AI algorithms often operate as complex black boxes, making it difficult to understand how they reach their decisions. The lack of interpretability and explainability in AI systems raises concerns about transparency, accountability, and potential biases. Users and stakeholders may need to understand the decision-making process of AI algorithms to ensure fair and ethical outcomes. Developing techniques and methods to make AI algorithms more interpretable and explainable is a technical challenge that needs to be addressed to foster trust and understanding of AI systems.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
Algorithmic bias refers to the unjust or discriminatory outcomes produced by AI systems due to biased or discriminatory data or design choices. AI algorithms can unintentionally reflect and perpetuate societal biases, leading to unfair treatment of individuals or groups. Addressing algorithmic bias and ensuring fairness in AI decision-making is a technical challenge that requires careful examination of training data, algorithm design, and evaluation methodologies. Techniques such as debiasing strategies and fairness-aware learning algorithms can help mitigate algorithmic bias and promote equitable outcomes.
Robustness and Reliability
AI systems must be robust and reliable to function effectively and ethically. Robustness refers to a system’s ability to perform consistently and accurately in different conditions and scenarios. AI algorithms should be able to handle new or unforeseen situations without experiencing significant performance degradation or introducing errors. Additionally, ensuring the reliability of AI systems is crucial to avoid potential failures or malfunctions that can have severe consequences. Developing robust AI algorithms and systems through rigorous testing, validation, and continuous monitoring is a key technical challenge in the field.

This image is property of lasserouhiainen.com.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Intellectual Property Rights
As AI technologies continue to advance, the question of intellectual property rights arises. Innovative AI algorithms or applications may be subject to patent or copyright protection, but determining the ownership and exclusivity of AI-generated outputs can be challenging. AI systems often learn from and generate intellectual property based on large datasets, making it difficult to clearly determine the contributions of humans and machines. Developing legal frameworks and regulations that address the unique challenges posed by AI-generated intellectual property is crucial to foster innovation while protecting the interests of creators and society as a whole.
Liability and Accountability
Determining liability and accountability when AI systems cause harm or make mistakes is a complex legal challenge. Traditional legal frameworks may not be well-equipped to handle the unique characteristics of AI technologies, such as their autonomy and lack of human agency. Assigning liability to developers, users, or the AI system itself requires careful consideration of factors such as foreseeability, control, and intentionality. Establishing clear legal frameworks that define the rights, responsibilities, and liabilities of different parties involved in the development and use of AI systems is essential for ensuring legal certainty and protecting individuals and society.
Regulation of Autonomous Systems
AI technologies that operate autonomously, such as autonomous vehicles or robots, present regulatory challenges. Ensuring the safety, reliability, and ethical behavior of autonomous systems require comprehensive regulations that cover areas such as testing, certification, and deployment. Determining the appropriate level of regulation to balance innovation and safety is a complex task. Striking the right balance between allowing for technological advancements while protecting human lives and interests is crucial in the regulation of autonomous systems.
Data Ownership and Privacy Laws
AI relies on vast amounts of data to train and operate effectively, which raises questions about data ownership and privacy. Organizations and individuals may have legitimate concerns about the use, access, and control of their data in AI systems. Additionally, AI technologies may collect and analyze personal data, requiring compliance with data protection and privacy laws. Developing clear legal frameworks that address data ownership, consent, and privacy in the context of AI is crucial to protect individual rights and ensure responsible use of data.
Social and Economic Challenges
Labor Market Disruptions
The adoption of AI technologies has the potential to disrupt labor markets, leading to significant changes in employment patterns and job availability. AI can automate routine and repetitive tasks, potentially leading to job displacement in certain industries. This disruption can have social and economic implications, including increased unemployment rates and income inequalities. Effective policies and strategies that address the potential job disruptions and facilitate the transition to new employment opportunities are essential to mitigate the negative impact on individuals and communities.
Impact on Education and Skills
The widespread adoption of AI technologies also raises challenges in education and skills development. As job requirements evolve, individuals need to acquire new skills and adapt to the changing demands of the workforce. Providing access to quality education and training programs that equip individuals with the necessary technical and cognitive skills is crucial. Additionally, fostering a culture of lifelong learning and promoting the development of skills that complement AI technologies, such as creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence, can help individuals thrive in the AI-driven world.
Unequal Access to AI Technology
Access to AI technology is not evenly distributed, which can exacerbate existing inequalities. Limited access to AI tools and resources can result in a digital divide, leaving certain individuals or communities at a disadvantage. This can have profound implications for education, employment, health, and overall socioeconomic well-being. Bridging the digital divide and ensuring equal access to AI technology and opportunities is essential to avoid widening disparities and promote inclusive growth.
Potential for Increased Inequality
While AI has the potential to improve efficiency and productivity, there is a concern that it may also contribute to increased inequality. The benefits of AI technologies, such as high-skilled job opportunities or improved healthcare, may not be evenly distributed across society. If access to AI tools and benefits is concentrated among specific individuals or groups, it can widen existing inequalities. Implementing policies and strategies that promote inclusive development, equity, and equal opportunities can help mitigate the potential for increased inequality due to AI adoption.
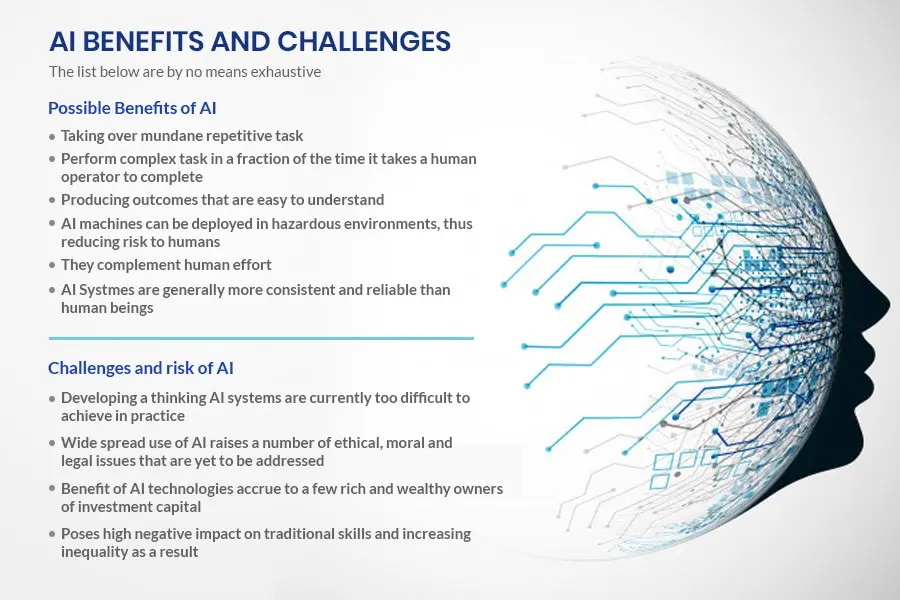
This image is property of www.bbntimes.com.
Safety Challenges
Accurate Risk Assessment
The safety of AI systems is paramount, and accurate risk assessment is crucial to identify and mitigate potential risks or harms. Understanding the limitations, vulnerabilities, and failure modes of AI algorithms and systems is necessary to prevent accidents, errors, or unintended consequences. Developing robust risk assessment methodologies that encompass various domains and applications of AI is a safety challenge that requires interdisciplinary research, rigorous testing, and ongoing monitoring.
Loss of Control and Unintended Consequences
As AI technologies become more autonomous and capable of learning and making decisions independently, the potential for unintended consequences or loss of control increases. Without proper safeguards, AI systems may exhibit unexpected behaviors or make decisions that are not aligned with human intentions or values. Ensuring human oversight, transparency, and accountability in the design and deployment of AI systems is crucial to mitigate the risks associated with loss of control and unintended consequences.
Cybersecurity Threats
AI technologies are not immune to cybersecurity threats, and the increasing reliance on AI systems introduces new attack vectors and vulnerabilities. Malicious actors can exploit vulnerabilities in AI algorithms or systems to manipulate data, introduce malicious behavior, or gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. Securing AI systems and protecting them from cybersecurity threats require robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, authentication, and continuous monitoring. Developing AI technologies with built-in security features and ensuring robust cybersecurity practices are crucial to maintain the integrity and safety of AI systems.
Autonomous Weapons and Warfare
The development and deployment of autonomous weapons pose significant safety and ethical challenges. AI technologies in the context of military applications can enable deadly autonomous systems that operate without direct human control. The potential consequences of such weapons, including accidental harm or misuse, raise concerns about ethical and legal accountability. International regulations that address the development and use of autonomous weapons, including clear guidelines and restrictions, are necessary to ensure safety, prevent arms races, and protect civilians in times of conflict.
Human-AI Collaboration Challenges
Trust and Acceptance
Building trust and acceptance in AI systems is essential for their effective integration into various domains and applications. Trust is necessary to ensure user adoption, cooperation, and reliance on AI technologies. Factors such as transparency, explainability, and track records of AI systems can influence trust and acceptance levels. Human-AI collaboration should focus on fostering trust by designing systems that are reliable, predictable, and transparent, addressing concerns and allowing users to understand and verify the decisions made by AI.
Transparency and Understandability
The lack of transparency and understandability in AI systems can hinder their effective collaboration with humans. Users and stakeholders may struggle to comprehend how AI algorithms arrive at their decisions, which can undermine trust and limit cooperation. Enhancing transparency and understandability by using interpretable algorithms, providing user-friendly explanations, and incorporating humans in the decision-making process can lead to effective collaboration and greater acceptance of AI technologies.
Ergonomics and User Experience
AI systems need to be designed with human-centered principles and considerations to optimize user experience and interaction. User interfaces must be intuitive, easy to use, and designed to accommodate users’ diverse needs and capabilities. Ergonomics and human factors research can help create AI systems that enhance user productivity, convenience, and satisfaction. Considering user feedback, preferences, and usability studies in the design and development of AI technologies can promote effective human-AI collaboration.
Job Redesign and Skill Enhancement
As AI technologies are integrated into workplaces, job roles and tasks may need to be redesigned to maximize the benefits of human-AI collaboration. Identifying tasks that are best suited for AI systems and those that require human judgment, creativity, or empathy can lead to more productive and fulfilling work experiences. Moreover, fostering a culture of continuous learning and providing opportunities for skill enhancement can empower individuals to adapt to changing work environments and effectively collaborate with AI technologies.

This image is property of www.artiba.org.
Data Challenges
Data Bias and Discrimination
Data used to train AI algorithms may reflect existing biases and discrimination present in society. Biased data can lead to biased AI systems and outcomes. It is essential to address data bias and discrimination by carefully selecting, cleaning, and augmenting datasets. Adopting methodologies that detect and mitigate biases can also contribute to more fair and equitable AI systems.
Data Privacy and Protection
The collection, storage, and analysis of vast amounts of personal data raise concerns about privacy and data protection. AI systems often require access to sensitive and personal information, and ensuring compliance with privacy laws and regulations is crucial. Implementing strong data encryption, anonymization techniques, and access controls can help protect individuals’ privacy while enabling the development and use of AI technologies.
Data Governance and Regulation
Data governance frameworks and regulations are necessary to guide the responsible and ethical use of AI technologies. These frameworks should address issues such as data sharing, data ownership, and data protection. Encouraging open and transparent data practices, establishing standards for data quality, and promoting responsible data stewardship are essential for effective and ethical AI development.
Data Storage and Management
AI technologies generate and consume vast amounts of data, posing challenges in terms of data storage and management. Efficient data storage infrastructure, including cloud computing and data centers, is required to support the growing data requirements of AI applications. Simultaneously, ensuring data security, accessibility, and integrity throughout the entire data lifecycle is crucial. Developing scalable and secure data management solutions is necessary to support the continuous growth of AI technologies.
Ethical Considerations in AI Development
Informed Consent and Data Usage
Respecting individuals’ autonomy and privacy rights, informed consent should be obtained before collecting and using personal data in AI systems. Users should have a clear understanding of how their data will be used and the potential implications. Implementing transparent data usage policies and informed consent mechanisms can promote ethical data practices and trust between AI developers and users.
Fairness and Non-discrimination
AI systems should be designed to ensure fairness and non-discrimination in decision-making processes. This requires addressing bias in both the training data and the algorithms themselves. Algorithms and models should be evaluated for fairness across different demographic groups and sensitive attributes. Regular audits and ongoing monitoring can help identify and rectify potential biases.
Avoiding Harming Humans
Developers need to ensure that AI systems do not cause harm or infringe upon human rights. Building safety features, fail-safe mechanisms, and risk assessment protocols are crucial to prevent accidents or unintended consequences. Ethical considerations and responsible development practices should be prioritized throughout the entire AI development process.
Benefit and Distribution Equity
The benefits and impact of AI technologies should be distributed equitably across society. Mitigating potential inequalities and ensuring that marginalized communities benefit from AI advancements require intentional efforts. Policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders must work collaboratively to identify and address systemic biases, gaps in access, and opportunities for inclusive and widespread benefits.

This image is property of www.mdis.edu.sg.
Societal Impact of AI
Job Displacement and Creation
The adoption of AI technologies may result in the displacement of certain jobs, but it can also create new job opportunities. While routine and repetitive tasks may be automated, there is a growing demand for skills related to AI, data analysis, and human-AI collaboration. Ensuring effective job transition and fostering skill development programs are necessary to manage the impact of AI on employment.
Education and Workforce Development
AI technologies can revolutionize education and enhance workforce development. AI-enabled personalized learning platforms can adapt to individual students’ needs, improving educational outcomes. Additionally, AI can provide insights and recommendations to support lifelong learning and professional development. Investing in AI-driven educational tools and promoting digital literacy can contribute to a more skilled and adaptable workforce.
Healthcare and Quality of Life
AI has the potential to transform healthcare by improving diagnostics, personalized medicine, and patient care. AI technologies can analyze vast amounts of medical data to identify patterns, assist in diagnosis, and enable early interventions. Intelligent healthcare monitoring systems can enhance patient safety and improve quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions. Harnessing the potential of AI in healthcare requires collaboration between healthcare providers, researchers, and AI developers while ensuring privacy and ethical considerations.
Surveillance and Privacy Concerns
The widespread use of AI in surveillance and monitoring raises concerns about privacy and civil liberties. AI-powered surveillance systems, such as facial recognition, can potentially infringe upon individuals’ privacy rights and enable mass surveillance. Striking a balance between public safety and privacy protection is critical. Implementing robust regulations, transparency, and ethical guidelines can help address these concerns and ensure the responsible use of AI in surveillance.
Addressing AI Challenges
Developing Ethical Frameworks and Guidelines
To address the ethical challenges posed by AI technologies, it is essential to develop ethical frameworks and guidelines. These frameworks should provide principles and standards for responsible AI development and deployment. They should address issues such as fairness, transparency, accountability, and human values. Promoting interdisciplinary collaboration involving ethicists, scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders can contribute to the development of comprehensive ethical frameworks.
Enhancing Transparency and Explainability
Transparency and explainability are essential for building trust and understanding in AI systems. Researchers and developers should strive to make AI algorithms and systems more transparent and explainable. This can be achieved through techniques such as opening up the algorithms to scrutiny, providing user-friendly explanations, or creating understandable interfaces. Enhancing transparency and explainability can contribute to better accountability, ethical decision-making, and user acceptance of AI technologies.
Advancing Data Privacy and Security Measures
To address the privacy and security challenges associated with AI, it is crucial to advance data privacy and security measures. Encouraging the use of privacy-enhancing technologies, adopting strong encryption methods, and promoting secure data handling practices can help protect individual privacy. Collaboration between technology companies, policymakers, and privacy advocates is necessary to establish robust data privacy and security standards.
Promoting Interdisciplinary Research and Collaboration
Addressing the challenges of AI requires interdisciplinary research and collaboration. Bringing together experts from various fields such as computer science, ethics, law, psychology, and social sciences can lead to a comprehensive understanding of the opportunities and risks associated with AI technologies. Collaboration between academia, industry, and policymakers is crucial to ensure the responsible and ethical development, deployment, and regulation of AI systems.