Can AI Be Regulated Or Is It A Dream?

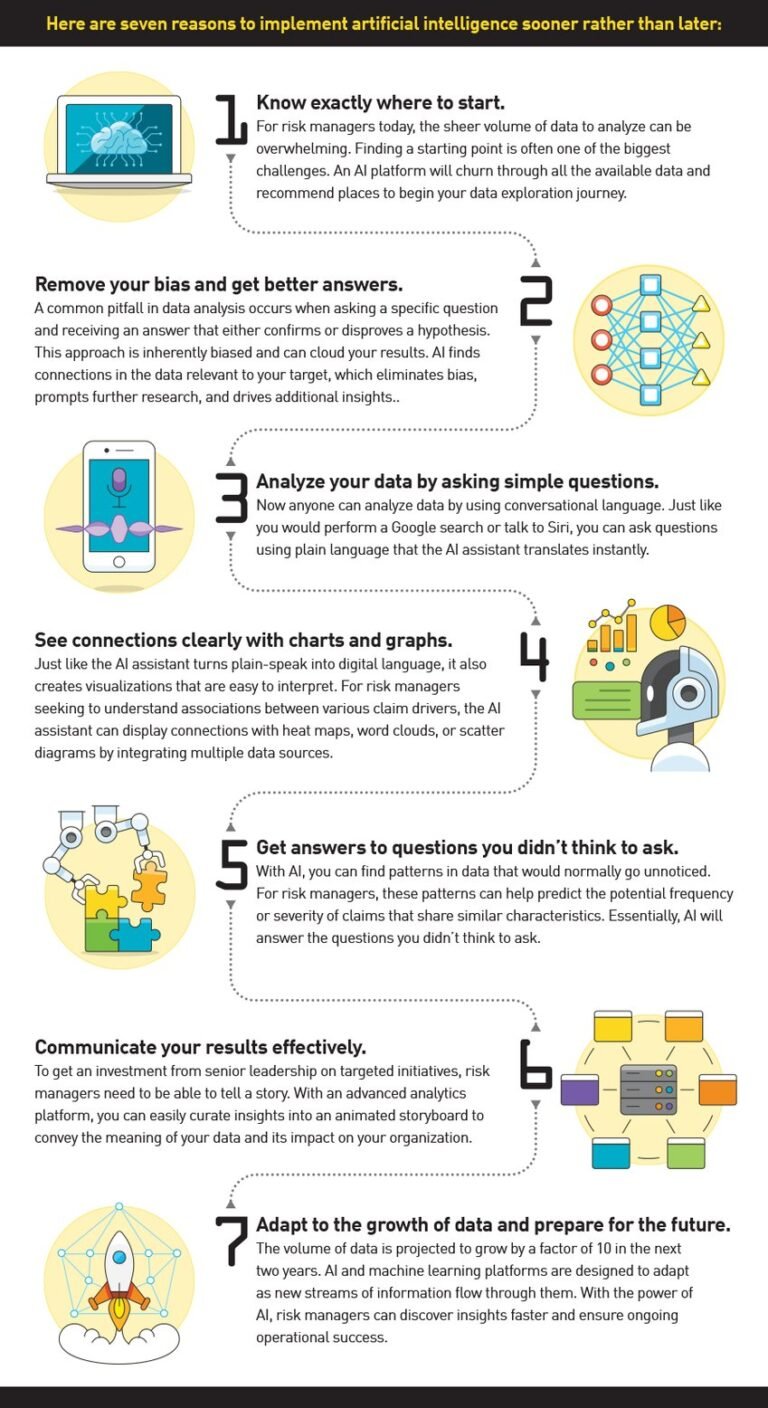
In today’s rapidly advancing technological era, the question of regulating artificial intelligence (AI) has become a subject of intense debate and speculation. With AI systems infiltrating various aspects of our lives, from healthcare to transportation, the need to establish regulations to govern its development and application has never been more crucial. However, the complexity and unpredictability of AI technology pose significant challenges for regulators, leading some to question if effective regulation is merely a distant dream. This article delves into the contentious issue of regulating AI, exploring the potential benefits and obstacles that lie ahead in achieving this ambitious goal.

The Current State of AI Regulation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of our lives, with its applications ranging from personal assistants like Siri to complex autonomous systems used in healthcare, finance, and transportation. As AI continues to evolve and permeate various sectors, the need for regulation has become increasingly important. The current state of AI regulation is characterized by a combination of existing regulations, ongoing challenges, and a growing recognition for the need of comprehensive AI regulation.
The existing regulations for AI
Currently, there is no single comprehensive regulation specifically designed for AI. However, several existing regulations provide a framework for addressing certain aspects of AI. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe aims to protect individuals’ privacy and personal data, which is particularly relevant in the context of AI systems that process vast amounts of data. Additionally, various industry-specific regulations exist, such as regulations governing autonomous vehicles or medical devices that incorporate AI.
Challenges in regulating AI
Regulating AI presents unique challenges due to its complex and dynamic nature. AI systems often involve machine learning algorithms that evolve and adapt over time, making it difficult to define clear boundaries for regulation. Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancements poses challenges for regulators, as they struggle to keep up with the latest developments and ensure that regulations remain relevant. Balancing the need for regulation with the fostering of innovation is another challenge that regulators face.
The need for AI regulation
The rapid growth and widespread adoption of AI technologies have raised concerns about their ethical implications, potential risks, and impact on society. Without appropriate regulation, there is a risk of unintended consequences, misuse of AI, and exacerbation of existing inequalities. To ensure the responsible development and deployment of AI, regulation is necessary to establish guidelines, standards, and accountability frameworks. Effective regulation can help address ethical concerns, protect data privacy and security, and mitigate the social impact of AI.
Arguments for Regulating AI
Ethical concerns and potential risks
One of the primary arguments for regulating AI is the ethical concerns associated with its applications. AI systems have the potential to make decisions and take actions that can have a profound impact on individuals and society. Ethical considerations such as fairness, transparency, and accountability need to be addressed to prevent biases, discrimination, and unintended harm. Regulation can help ensure that AI systems are developed and used in a manner aligned with ethical principles, protecting the rights and well-being of individuals.
Social impact and inequality
AI has the potential to shape society in profound ways, affecting employment, healthcare, education, and more. Without proper regulation, there is a risk of exacerbating existing social inequalities. For example, AI-driven automation can lead to job displacement, disproportionately impacting certain groups. Regulation can play a crucial role in ensuring that AI technologies are developed and deployed in a way that promotes fairness, inclusivity, and social well-being.
Data privacy and security
AI systems rely on vast amounts of data for training and decision-making. This raises concerns about data privacy and security. Regulation can help establish safeguards and guidelines to protect personal data, ensure consent mechanisms are in place, and prevent unauthorized access or misuse of data. By addressing data privacy and security concerns, regulation can foster trust in AI technologies and facilitate their widespread adoption.
Arguments Against Regulating AI
Innovation and economic growth
Opponents of AI regulation argue that excessive regulation can stifle innovation and hinder economic growth. They argue that the dynamic nature of AI requires flexibility and adaptability, which may be hampered by burdensome regulatory requirements. Additionally, they contend that regulation could result in higher costs and bureaucratic processes, discouraging investment and hindering the development of AI technologies.
The complexity of AI systems
AI systems, particularly those based on machine learning algorithms, can be complex and difficult to understand. Opponents of regulation argue that the complexity of these systems makes it challenging to establish clear and effective regulatory frameworks. They contend that a one-size-fits-all approach may not be suitable for regulating AI and that the dynamic nature of AI calls for more flexible and adaptive approaches.
Fear of stifling technological progress
Another argument against regulating AI is the fear that excessive regulation could impede technological progress. Proponents of this view contend that AI has the potential to revolutionize various industries and improve the quality of life. They argue that overregulation could discourage experimentation, slow down innovation, and hinder the advancements that AI can bring.

Existing Frameworks for AI Regulation
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR, implemented in Europe, provides a comprehensive framework for protecting individuals’ privacy and personal data. Although not specifically designed for AI, it has significant implications for AI systems due to their reliance on personal data. The GDPR emphasizes transparency, consent, and accountability in data processing, providing a foundation for addressing data privacy concerns associated with AI.
Ethics guidelines and principles
Various organizations and initiatives have developed ethics guidelines and principles for AI. For example, the IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems has developed Ethically Aligned Design principles, which emphasize the importance of human well-being, transparency, and accountability. These guidelines provide a starting point for addressing ethical concerns in AI and can inform future regulatory frameworks.
Industry-specific regulations
Certain industries have specific regulations in place to address the unique challenges posed by AI. For example, the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles are subject to regulation by transportation authorities. Similarly, the use of AI in healthcare is regulated by bodies such as the FDA. These industry-specific regulations provide a targeted approach to addressing the risks and challenges associated with AI in specific domains.
Potential Approaches and Strategies for AI Regulation
Risk-based regulation
A risk-based approach to regulation involves assessing the potential risks associated with AI and tailoring regulations accordingly. This approach allows regulators to focus on areas with higher risks, thereby ensuring that regulatory efforts are targeted and effective. By prioritizing risks and focusing on mitigating them, risk-based regulation strikes a balance between addressing concerns and fostering innovation.
Transparency and explainability requirements
Regulatory frameworks can include requirements for transparency and explainability of AI systems. These requirements ensure that AI systems are not opaque “black boxes” and enable individuals to understand the rationale behind AI-driven decisions. Transparent and explainable AI can help build trust, facilitate accountability, and mitigate the potential risks associated with biased or discriminatory outcomes.
International collaboration and standards
Given the global nature of AI, international collaboration and the establishment of common standards are crucial for effective regulation. Collaboration between countries and organizations can help share best practices, exchange knowledge, and harmonize regulations. Common standards can ensure consistency, interoperability, and accountability across borders, facilitating the ethical and responsible development of AI on a global scale.
The Role of Government and Policy-makers
Creating regulatory bodies and frameworks
Government bodies can play a pivotal role in regulating AI by creating dedicated regulatory bodies and frameworks. These bodies would be responsible for developing and implementing regulations, ensuring compliance, and monitoring the impact of AI technologies. By establishing clear regulatory frameworks, governments can provide certainty and guidance for individuals, organizations, and AI developers.
Establishing guidelines and standards
Governments can also contribute to AI regulation by establishing guidelines and standards. These guidelines can provide clarity on ethical considerations, data privacy, and security requirements. Standards can foster interoperability, facilitate the responsible development of AI, and ensure that AI technologies adhere to the necessary criteria for transparency, explainability, fairness, and accountability.
Encouraging innovation and responsible development
Government policies can strike a balance between regulation and fostering innovation. By providing incentives, funding research and development, and supporting startups, governments can encourage the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies. Collaborative initiatives between governments, academia, and the private sector can support innovation while ensuring adherence to regulatory principles and ethical considerations.
Industry Self-regulation in AI
Voluntary codes of conduct
Industry self-regulation can complement government regulation by encouraging responsible AI practices. Voluntary codes of conduct can outline ethical principles, guidelines, and best practices for AI developers and organizations. These codes can promote transparency, fairness, and accountability, fostering a culture of responsible AI development and use within the industry.
Ethics committees within organizations
To ensure responsible AI practices, organizations can establish ethics committees or similar bodies. These committees can provide guidance on ethical considerations, assess the potential risks associated with AI applications, and ensure compliance with ethical principles. By integrating ethical considerations into their structure and decision-making processes, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to responsible AI development.
Promoting responsible AI practices
Industry associations and organizations can take an active role in promoting responsible AI practices. Through educational initiatives, conferences, and workshops, they can raise awareness about the ethical implications of AI and provide guidance on best practices. By fostering a culture of responsible AI development, organizations can contribute to the overall effort of ensuring ethical and accountable use of AI technologies.
Challenges in Implementing AI Regulation
Keeping up with rapid advancements
One of the significant challenges in AI regulation is the rapid pace of advancements. AI technologies evolve quickly, making it challenging for regulatory frameworks to keep pace. To address this challenge, regulation needs to be adaptable, flexible, and future-proof. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are necessary to ensure that regulations remain relevant and effective in the face of technological advancements.
Enforcement and monitoring
Enforcing AI regulations presents its own set of challenges. AI systems can be complex and difficult to understand, making it difficult to identify violations or assess compliance. Monitoring the use of AI technologies and ensuring adherence to regulations require expertise and resources. Regulatory bodies need to be adequately staffed and equipped to effectively enforce regulations, detect non-compliance, and take corrective actions when necessary.
Balancing regulation with innovation
Striking the right balance between regulation and innovation is a delicate challenge. Excessive regulation can stifle innovation, discourage investment, and limit the potential benefits of AI technologies. On the other hand, inadequate regulation can result in ethical concerns, risks, and negative societal impacts. Achieving the right balance requires a collaborative effort between governments, industry stakeholders, and policymakers to foster innovation while ensuring responsible development and use of AI technologies.
The Future of AI Regulation
Predictions and speculations
The future of AI regulation is subject to speculation and predictions. As AI continues to advance, it is likely that new regulations specific to AI will emerge. The focus may shift towards addressing the ethical concerns and societal impact of AI, harmonizing international regulations, and establishing global standards. The role of AI ethics committees, industry self-regulation, and collaborative initiatives is likely to expand in shaping the regulatory landscape.
Potential scenarios and impacts
The future of AI regulation can take various forms, depending on the direction taken by governments, regulators, and industry players. Potential scenarios include increased transparency and explainability requirements for AI systems, stricter data privacy and security regulations, and enhanced accountability frameworks. The impact of AI regulation could include improved trust in AI technologies, reduced risks and biases, and greater social acceptance and adoption of AI.
Continued discussions and evolving frameworks
As AI continues to evolve and its impact on society becomes more pronounced, the need for ongoing discussions and evolving frameworks for regulation will remain crucial. The collaborative efforts between various stakeholders, including governments, industry, academia, and civil society, will shape the future of AI regulation. Continued dialogue, knowledge sharing, and iterative improvements in regulatory frameworks will be essential in ensuring the responsible and ethical development and use of AI.
Conclusion
The necessity of regulating AI is becoming increasingly apparent as its applications and influence continue to grow. Ethical concerns, potential risks, social impact, and data privacy considerations underline the need for comprehensive AI regulation. While there are arguments against regulation, striking the right balance between fostering innovation and addressing societal concerns is crucial. Existing frameworks and industry self-regulation initiatives provide a foundation for future regulatory frameworks. Collaborative efforts between governments, regulators, industry, and academia will play a vital role in the ongoing evaluation and evolution of AI regulation. By ensuring responsible development, transparency, and accountability, AI regulation can foster trust, mitigate risks, and maximize the benefits of AI technologies.